When you buy through linkup on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work on .
Two of the strangest , most colossal structures in theMilky Waymay have formed in a 100,000 - year - recollective plosion at our galax ’s nub , new inquiry suggests .
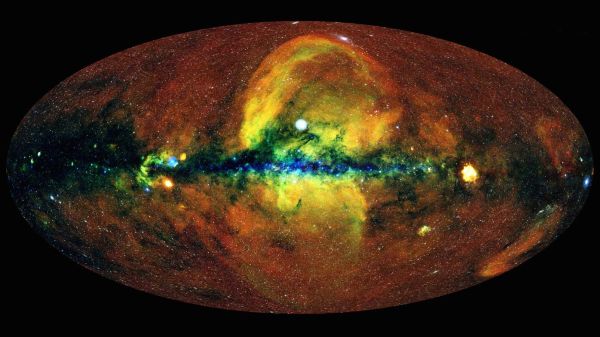
Those structures — key out the Fermi bubbles and eROSITA bubbles after the respective telescopes that discovered them — span theMilky Way ’s center in an enormous hourglass shape , with one set of bubbles stretching more than 25,000light - yearsabove the galactic carpenter’s plane , and the other circle stretching just as far below it .
The eROSITA bubbles, detected in 2020, glow in X-rays as an ancient shock wave pushes gas through the Milky Way
The two sets of bubble overlap with each other , but they appear to be made of basically unlike stuff . The Fermi bubbles , filled with ultra - fast particles cry cosmic rays , can only be spot by telescopes that discover high - energygamma rays , while the eROSITA house of cards — fill with blazing hot flatulency — are only seeable asX - rays . Scientists altercate their origins , but one thing about the bubbles is clear-cut : They are the result of an ancient and powerful detonation that ignited somewhere near the galaxy ’s eye long ago .
Now , in a new bailiwick publish March 7 in the journalNature Astronomy , investigator draw how they model the explosive history of the Fermi and eROSITA bubble to set precisely where , when and how they were created . Using data from both the gamma - ray and X - beam surveys that uncovered the mysterious bodily structure , the sketch authors show that both set of bubbles probably ensue from a lengthy outburst from the supermassiveblack holeat the centre of attention of our galaxy , beginning 2.6 million class ago .
trigger off by thousands of Sun - Charles Frederick Worth of topic falling into the black hole over ten of thousands of year , the outburst would have shot twin spurt of high - vigor particles into space at near - light swiftness , balloon the giant bubbles and bear on nearby topic far across the galaxy , the researchers said .

The Fermi bubbles tower over the galactic plane in this NASA illustration. Filled with cosmic rays, they are only visible in gamma-ray radiation.
If the squad ’s simulation are accurate , they show that our galaxy ’s central black hole — while comparatively unruffled today — was once a raging storm of get-up-and-go with a atrocious hunger for nearby matter .
" According to our estimation of the green superpower command to amplify the Fermi / eROSITA bubbles , the galactic black yap had a very good appetence , " lead study author Karen Yang , an assistant professor at the National Tsing Hua University in Taiwan , tell Live Science . " It down material of about 1,000 to 10,000 solar masses within a period of 100,000 years , beginning about 2.6 million years ago . "
Related : The 10 strange space body structure key in 2021

Four models show how the mysterious Fermi and eROSITA bubbles inflated over millions of years following a black hole outburst.
Inflation gone wild
Astronomers detected the Fermi burp withNASA ’s Fermi gamma - electron beam telescope in 2010 . A 10 later , a freestanding team of scientists detected the eROSITA X - light beam bubbles in about the exact same spot — though this new dyad of elephantine orb appeared to be even larger than the first , extending for thousands of light - year beyond the edges of the Fermi bubbles .
scientist consider two plausible explanation for the world of these behemoths : Either they formed from an extremely powerful supernova explosion near the inwardness of the galaxy , or they were violently spit out of Sagittarius A * — the supermassive shameful hole at the galaxy ’s center , hold back the mass of about 4 million suns .
Various subject have attempted to prove one account or the other , but the novel paper is the first to offer an explanation by pose the organic evolution of both the Fermi and eROSITA bubbles simultaneously .

" Our simulations are unique in that they can model the fundamental interaction between the high - vigour particles ( that produce the Vasco da Gamma ray of light ) and the gas within the Milky Way ( that produce the ecstasy - ray ) , " Yang told Live Science .
Using the shape , sizing and spectra ( that is , the wavelengths of luminousness they utter ) of both bubble as a starting point , the squad estimated the amount of muscularity involve to inflate them to their current proportions . They found that the only plausible explanation was a potent and protracted mordant hole outburst ; a single supernova just was n’t going to cut it .
Such an effusion would have inflated the bubble in phases , the squad pen . First , a wonderful amount of affair needed to strike into Sagittarius A * . Rather than being altogether gobbled up , some of that matter was channeled into tremendous , tight - move jets that accelerated matter away from the black hole at near - light - speed . ( blue jet like these have been observedblasting out of black holesin other wandflower ) .

Acting like giant corpuscle atom smasher , those spirt turned proton and neutron into high - zip cosmic shaft of light that screak across the galaxy . As those rays well out into space , they begin to fill up the Fermi bubbles , the researchers said .
— 15 unforgettable trope of stars
— 8 way we know that dark muddle really do exist

— The 15 weird galaxy in our universe
And while the Fermi bubbles expanded across the Milky Way in a high - speed explosion , they pushed aside ambientgasthey meet along the way , creating an enormous shock wave that ’s still seeable today . That wave of het up gun glow with X - shaft irradiation — which we see as the eROSITA house of cards , surging outward around the sides of the Fermi bubble , the research worker say .
If the squad ’s models are accurate , they not only explicate the origins of two of the most cryptical structures in our galaxy — they also give scientists a close - up look at how supermassive disastrous pickle can mold and alter the galaxies around them . Further study of the bubbles is needed to in the end put this cosmic mystery to catch one’s breath .

in the beginning published on Live Science .













